Workflow for Acropora pulchra de novo transcriptome
Designing a workflow to create a de novo transcriptome for Acropora pulchra
Goal:
Important notes about de novo transcriptomes
- Raghavan et al. 2022
- “A simple guide to de novo transcriptome assembly and annotation”
- De novo transcriptome assembly, in contrast, is ‘reference-free’. The process is de novo (Latin for ‘from the beginning’) as there is no external information available to guide the reconstruction process. It must be accomplished using the information contained in the reads alone.
- This approach is useful when a genome is unavailable, or when a reference-guided assembly is undesirable.
- For instance, in opposition to a de novo assembler successfully producing a transcript, a reference-guided approach might not be able to reconstruct it correctly if it were to correspond to a region on the reference containing sequencing or assembly gaps [15, 16].

Acropora genomes
- Shinzato et al. 2011
- First Acropora genome sequenced was Acropora digitifera in “Using the Acropora digitifera genome to understand coral responses to environmental change”
- Shinzato et al. 2020
- Sequenced genomes of 15 Acropora species (A. acuminata, A. awi, A. cytherea, A. digitifera, A. echinata, A. florida, A. gemmifera, A. hyacinthus, A. intermedia, A. microphthalma, A. muricata, A. nasta, A. selago, A. tenuis, and A. yongei)
Acropora de novo assemblies and notes
- Oldach and Vize 2018
- De novo assembly and annotation of the Acropora gemmifera transcriptome
-
Used Trintiy to assemble 31.6 million combined raw reads and built into 104,000 contigs
- Kitchen et al. 2015
- De Novo Assembly and Characterization of Four Anthozoan (Phylum Cnidaria) Transcriptomes
Other de novo transcriptome resources
- Wong and Putnam Porites astreoides genome
- GitHub
- Structural annotation of the P. astreoides genome was completed on the University of Rhode Island High Performance Computer ‘Andromeda’. As input for MAKER v3.01.03 (RRID:SCR_005309) [64] we used an existing P. astreoides transcriptome from samples collected in the Florida Keys, USA [32] and existing congener P. lutea peptide sequences from a sample collected in Australia [57].
- Chui et al. 2020
- “De novo transcriptome assembly from the gonads of a scleractinian coral, Euphyllia ancora: molecular mechanisms underlying scleractinian gametogenesis”
Trinity Resources and Vignette
Acropora pulchra Gametogenesis transcriptome data files on URI andromeda:
Location on Andromeda, the HPC server for URI:
cd /data/putnamlab/KITT/hputnam/20230825_Bermuda_Reference_Transcriptomes/
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
Copied all data files to new location on Andromeda
cp -r /data/putnamlab/KITT/hputnam/20230825_Bermuda_Reference_Transcriptomes/ACRP* /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
Acropora pulchra E5 Rules of Life project transcriptome data files on University of Washington OWL data storage HPC database
Location on OWL, the HPC server for UW:
https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/A_pulchra/30-789513166/
Downloaded all files to Andromeda URI HPC location
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/
wget -r -nd -A .fastq.gz https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/A_pulchra/30-789513166/
wget -r -nd -A .md5 https://owl.fish.washington.edu/nightingales/A_pulchra/30-789513166/
ACR-140_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACR-140_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACR-145_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACR-145_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACR-150_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACR-150_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACR-173_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACR-173_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACR-178_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz
ACR-178_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz
ACR-140_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-140_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-145_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-145_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-150_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-150_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-173_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-173_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-178_TP2_R1_001.fastq.gz.md5
ACR-178_TP2_R2_001.fastq.gz.md5
Samples QC and Qubit Results
| Tube Label | RNA_ng_µl | RNA_µl | RNA µg | Link to notebook post1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR-140_TP2 | 12 | 90 | 1.08 | https://kterpis.github.io/Putnam_Lab_Notebook/20211012-RNA-DNA-extractions-from-E5-project/ |
| ACR-145_TP2 | 20.8 | 87 | 1.8096 | https://kterpis.github.io/Putnam_Lab_Notebook/20211012-RNA-DNA-extractions-from-E5-project/ |
| ACR-150_TP2 | 13 | 87 | 1.131 | https://github.com/Kterpis/Putnam_Lab_Notebook/blob/master/_posts/2021-09-03-20210903-RNA-DNA-extractions-from-E5-project.md |
| ACR-173_TP2 | 11.4 | 87 | 0.9918 | https://kterpis.github.io/Putnam_Lab_Notebook/20211102-RNA-DNA-extractions-from-E5-project/ |
| ACR-178_TP2 | 12.2 | 87 | 1.0614 | https://github.com/Kterpis/Putnam_Lab_Notebook/blob/master/_posts/2021-09-02-20210902-RNA-DNA-extractions-from-E5-project.md |
| ACRP-CON | 43.2 | 24 | 1.0368 | https://github.com/daniellembecker/DanielleBecker_Lab_Notebook/blob/master/_posts/2023-04-25-Acropora-pulchra-transcriptome-extraction-concentration.md |
Workflow Steps
Trim ACRP-CON reads.
Reads for samples ACR-140, ACR-145, ACR-150, ACR-173, and ACR-178 were trimmed using the built-in version of Trimmomatic with the default settings, following the 9FastQ QC and Trimming - E5 Coral RNA-seq Data for A.pulchra protocol. All fast
Downloaded all files to Andromeda URI HPC location
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed
wget -r -nd -A .fastq.gz https://gannet.fish.washington.edu/Atumefaciens/20230519-E5_coral-fastqc-fastp-multiqc-RNAseq/A_pulchra/trimmed/
RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
1) Run FastQC on ACRP_R1 and ACRP_R2
a) Make folders for raw FastQC results and scripts
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/
mkdir fastqc_results
b) Write script for checking quality with FastQC and submit as job on Andromeda
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/fastqc_raw.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 24:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=100GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw
#SBATCH --error="script_error" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output="output_script" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
module load FastQC/0.11.9-Java-11
for file in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/*ACRP
do
fastqc $file --outdir /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptxome/2023_A.pul/data/fastqc_results/
done
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/fastqc_raw.sh
Submitted batch job 281440
Combined QC output into 1 file with MultiQC, do not need a script due to fast computational time
module load MultiQC/1.9-intel-2020a-Python-3.8.2
multiqc /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/fastqc_results/*fastqc.zip -o /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/fastqc_results/multiqc/
c) Copy MultiQC and FastQC files to local computer
scp -r danielle_becker@ssh3.hac.uri.edu:/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/fastqc_results/multiqc/multiqc_report.html /Users/Danielle/Desktop/Putnam_Lab/Gametogenesis/bioinformatics/transcriptome/original_fastqc
scp -r danielle_becker@ssh3.hac.uri.edu:/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/fastqc_results/*.html /Users/Danielle/Desktop/Putnam_Lab/Gametogenesis/bioinformatics/transcriptome/original_fastqc
4) Trim and clean reads
a) Make trimmed reads folder in all other results folders
mkdir data/trimmed
cd trimmed
c) Write script for Trimming and run on Andromeda
#Run fastp on files #Trims 20bp from 5’ end of all reads #Trims poly G, if present
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trim.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 24:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=100GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw
#SBATCH --error="script_error" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output="output_script" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
module load fastp/0.19.7-foss-2018b
array1=($(ls *ACRP_R1*.fastq.gz)) #Make an array of sequences to trim
for i in ${array1[@]}; do
fastp --in1 ${i} --in2 $(echo ${i}|sed s/_R1/_R2/) --detect_adapter_for_pe --trim_poly_g --trim_front1 20 --trim_front2 20 --out1 ../trimmed/${i} --out2 ../trimmed/$(echo ${i}|sed s/_R1/_R2/)
done
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trim.sh
Submitted batch job 281915
5) Check quality of trimmed files
a) Check number of files in /trimmed directory
ls -1 | wc -l
#12
b) Check number of reads in /trimmed directory and in /raw directory
# look at raw reads
zgrep -c "@A01587" ACRP* > seq_counts
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz:178057412
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz:178057412
# look at trimmed reads
zgrep -c "@A01587" ACRP* > trimmed_seq_counts
ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz:173194930
ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz:173194930
c) Run FastQC on trimmed data
mkdir trimmed_qc
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/fastqc_trimmed.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 24:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=100GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc
#SBATCH --error="script_error"
#SBATCH --output="output_script"
module load FastQC/0.11.8-Java-1.8
for file in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/ACRP*
do
fastqc $file --outdir /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc
done
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/fastqc_trimmed.sh
Submitted batch job 281933
d) Run MultiQC on trimmed data, Combined QC output into 1 file with MultiQC, do not need a script due to fast computational time
module load MultiQC/1.9-intel-2020a-Python-3.8.2
multiqc /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc/*fastqc.zip -o /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc/trimmed_multiqc
e) Copy multiqc and fastqc to computer, use terminal window fro desktop not in server
scp -r danielle_becker@ssh3.hac.uri.edu:/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc/trimmed_multiqc/multiqc_report.html /Users/Danielle/Desktop/Putnam_Lab/Gametogenesis/bioinformatics/transcriptome/trimmed_fastqc
scp -r danielle_becker@ssh3.hac.uri.edu:/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trimmed_qc/*.html /Users/Danielle/Desktop/Putnam_Lab/Gametogenesis/bioinformatics/transcriptome/trimmed_fastqc
6) Run Trinity with paired-end sequences
Trinity commands as found on Trinity vignette and Roberts Lab Guide:
- Trinity = runs trinity program
- seqType fq = specifys FASTQ file format
- SS_lib_type RF = Trinity has the option (–SS_lib_type) to specify whether or not the sequences you’re assembly are “stranded”. User should specify this in the following fasion as on option in the Trinity command (example specifies typical stranded libraries): –SS_lib_type RF
- max_memory 100G = max memory for trinity 100G should not be changed, per communications with the developer
- CPU 36 = match however many CPUs your computing cluster has access to, maximum number of parallel processes (for andromeda the maximum number of cores is 36. On Unity, the nodes in the uri-cpu partition can go up to 64, and in the cpu and cpu-preempt partitions it can go to 128)
- left = paired end reads filenames
- right = paired end reads filenames
- For non-stranded assembly, you do not provide any information about the directionality of the reads, allowing Trinity to assume an equal distribution of reads from both strands.
a) Originally ran both stranded and non-stranded in same assembly, running them separate beneath this code
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=20230925_trinity
#SBATCH --time=30-00:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed
#SBATCH --error="script_error" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output="output_script" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
# Load Trinity module
module load Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a
# Run Trinity
Trinity \
--seqType fq \
--SS_lib_type RF \
--max_memory 100G \
--CPU 36 \
--left \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz \
--right \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity.sh
Submitted batch job 282369 on 20230927 at 15:56
Trinity finished 20231011 with a FailedCommands.txt file. I submitted a GitHub issues with my output script to the Trinity GitHub Issues.
Response to issue:
It looks like there's 18 failed commands. I'm seeing the errors like this:
/glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_8/CBin_8455/c845648.trinity.reads.fa.out/inchworm.fa.tmp':
If you find the failed_commands.txt file (or similar name) in the trinity
output directory, it should have the list of the commands it's having a
hard time with. Each should have an output directory, like in the above
example, it would be:
/glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_8/CBin_8455/c845648.trinity.reads.fa.out
If you can remove those output directories and then rerun your Trinity
command, it should hopefully process everything just fine (unless you ran
out of disk space...)
I then removed all the corrupt files (18) listed in the FailedCommands.txt file and re-ran Trinity on 20231012 at 16:04 after changing the amount of CPUs to 20 because a number of solutions in the developer’s GitHub Issues suggest that sometimes the CPUs process things too quickly for the computer’s file system to keep up, leading to problems
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_8/CBin_8455/c845648.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_6/CBin_6008/c600976.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_8/CBin_8295/c829640.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_7/CBin_7785/c778615.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_0/CBin_139/c13942.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_7/CBin_7922/c792325.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_4/CBin_4006/c400692.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_3/CBin_3881/c388169.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_8/CBin_8455/c845648.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_5/CBin_5650/c565150.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_5/CBin_5326/c532719.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_6/CBin_6986/c698736.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_6/CBin_6598/c659988.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_6/CBin_6003/c600479.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_4/CBin_4526/c452745.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_2/CBin_2558/c255895.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_2/CBin_2424/c242423.trinity.reads.fa.out
rm -rf /glfs/brick01/gv0/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/trinity_out_dir/read_partitions/Fb_7/CBin_7230/c723106.trinity.reads.fa.out
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity.sh
Submitted batch job 285355
Trinity completed successfully!!!! When Trinity completes, it creates a ‘trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta’ output file (or prefix based on the output directory you specify).
Trinity groups transcripts into clusters based on shared sequence content. Such a transcript cluster is very loosely referred to as a ‘gene’. This information is encoded in the Trinity fasta accession. An example Fasta entry for one of the transcripts is formatted like so:
>TRINITY_DN1000_c115_g5_i1 len=247 path=[31015:0-148 23018:149-246]
AATCTTTTTTGGTATTGGCAGTACTGTGCTCTGGGTAGTGATTAGGGCAAAAGAAGACAC
ACAATAAAGAACCAGGTGTTAGACGTCAGCAAGTCAAGGCCTTGGTTCTCAGCAGACAGA
AGACAGCCCTTCTCAATCCTCATCCCTTCCCTGAACAGACATGTCTTCTGCAAGCTTCTC
CAAGTCAGTTGTTCACAGGAACATCATCAGAATAAATTTGAAATTATGATTAGTATCTGA
TAAAGCA
b) Run stranded assembly to provide Trinity with information about the directionality of the reads, allowing it to consider this information during the assembly process
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity_stranded.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=20240418_trinity_stranded
#SBATCH --time=30-00:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output
#SBATCH --error="script_error_stranded" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output="output_script_stranded" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
# Load Trinity module
module load Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a
# Run Trinity
Trinity \
--seqType fq \
--SS_lib_type RF \
--max_memory 100G \
--CPU 36 \
--left \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R1_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz \
--right \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-140-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-145-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-150-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-173-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz,\
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/RNA-ACR-178-S1-TP2_R2_001.fastp-trim.20230519.fastq.gz
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity_stranded.sh
Submitted batch job 312460 on 20240418 14:24
b) Run non-stranded assembly, do not provide any information about the directionality of the reads, allowing Trinity to assume an equal distribution of reads from both strands
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity_nonstranded.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=20240418_trinity_nonstranded
#SBATCH --time=30-00:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output
#SBATCH --error="script_error_nonstranded" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output="output_script_nonstranded" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
# Load Trinity module
module load Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a
# Run Trinity
Trinity \
--seqType fq \
--max_memory 100G \
--CPU 36 \
--left /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/ACRP_R1_001.fastq.gz \
--right /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trimmed/ACRP_R2_001.fastq.gz \
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/trinity_nonstranded.sh
Submitted batch job 312458 on 20240418 14:00
7) Assessing quality of the assessment
Use Trinity toolkit utilities for a assembly quality assessment
a) Run TrinityStats.pl script for stats output, need to use the path of trinity module and then add the util folder before you can access the .pl script
This script will compute the contig Nx statistics (eg. the contig N50 value), in addition to a modification of the Nx statistic that takes into consideration transcript expression (read support) data, which we call the ExN50 statistic.
Based on the lengths of the assembled transcriptome contigs, we can compute the conventional Nx length statistic, such that at least x% of the assembled transcript nucleotides are found in contigs that are at least of Nx length. The traditional method is computing N50, such that at least half of all assembled bases are in transcript contigs of at least the N50 length value.
Ran on original assembly:
/opt/software/Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a/trinityrnaseq-v2.15.1/util/TrinityStats.pl trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta > trinity_assembly_stats
################################
## Counts of transcripts, etc.
################################
Total trinity 'genes': 1019918
Total trinity transcripts: 1476390
Percent GC: 44.78
########################################
Stats based on ALL transcript contigs:
########################################
Contig N10: 4395
Contig N20: 2790
Contig N30: 1956
Contig N40: 1417
Contig N50: 1021
Median contig length: 376
Average contig: 675.99
Total assembled bases: 998026397
The N10 through N50 values are shown computed based on all assembled contigs. In this example, 10% of the assembled bases are found in transcript contigs at least 4,395 bases in length (N10 value), and the N50 value indicates that at least half the assembled bases are found in contigs that are at least 1,021 bases in length.
The contig N50 values can often be exaggerated due to an assembly program generating too many transcript isoforms, especially for the longer transcripts. To mitigate this effect, the script will also compute the Nx values based on using only the single longest isoform per ‘gene’:
#####################################################
## Stats based on ONLY LONGEST ISOFORM per 'GENE':
#####################################################
Contig N10: 3840
Contig N20: 2221
Contig N30: 1479
Contig N40: 1026
Contig N50: 731
Median contig length: 335
Average contig: 565.18
Total assembled bases: 576438524
You can see that the Nx values based on the single longest isoform per gene are lower than the Nx stats based on all assembled contigs, as expected, and even though the Nx statistic is really not a reliable indicator of the quality of a transcriptome assembly, the Nx value based on using the longest isoform per gene is perhaps better for reasons described above.
Ran on nonstranded and stranded assembly:
/opt/software/Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a/trinityrnaseq-v2.15.1/util/TrinityStats.pl trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta > trinity_assembly_stats_nonstranded
/opt/software/Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a/trinityrnaseq-v2.15.1/util/TrinityStats.pl trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta > trinity_assembly_stats_stranded
N50 nonstranded results:
################################
## Counts of transcripts, etc.
################################
Total trinity 'genes': 379192
Total trinity transcripts: 574858
Percent GC: 43.90
########################################
Stats based on ALL transcript contigs:
########################################
Contig N10: 5001
Contig N20: 3273
Contig N30: 2346
Contig N40: 1722
Contig N50: 1256
Median contig length: 415
Average contig: 771.09
Total assembled bases: 443268594
The N10 through N50 values are shown computed based on all assembled contigs. In this example, 10% of the assembled bases are found in transcript contigs at least 4,395 bases in length (N10 value), and the N50 value indicates that at least half the assembled bases are found in contigs that are at least 1,021 bases in length.
The contig N50 values can often be exaggerated due to an assembly program generating too many transcript isoforms, especially for the longer transcripts. To mitigate this effect, the script will also compute the Nx values based on using only the single longest isoform per ‘gene’:
## Stats based on ONLY LONGEST ISOFORM per 'GENE':
#####################################################
Contig N10: 3857
Contig N20: 2295
Contig N30: 1577
Contig N40: 1120
Contig N50: 815
Median contig length: 360
Average contig: 606.70
Total assembled bases: 230057536
N50 Results for stranded assembly
################################
## Counts of transcripts, etc.
################################
Total trinity 'genes': 670597
Total trinity transcripts: 982351
Percent GC: 44.73
########################################
Stats based on ALL transcript contigs:
########################################
Contig N10: 4414
Contig N20: 2858
Contig N30: 2047
Contig N40: 1498
Contig N50: 1073
Median contig length: 367
Average contig: 681.05
Total assembled bases: 669031487
#####################################################
## Stats based on ONLY LONGEST ISOFORM per 'GENE':
#####################################################
Contig N10: 3950
Contig N20: 2359
Contig N30: 1575
Contig N40: 1074
Contig N50: 747
Median contig length: 321
Average contig: 560.45
Total assembled bases: 375834024
b) Run BUSCO ( Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs)
- Commands and overview for running BUSCO here: https://busco.ezlab.org/busco_userguide.html
- uses highly conserved single-copy orthologs; evolutionary informed expectations of gene content.
-
appears that youu can focus a BUSCO analysis to orthologs related to your target taxa.
- image below shows a BUSCO analysis comparing the crayfish targetted for tde novo transcriptome assembly to 44 other arthropod species assemblies and a single vertebrate assembly:
Theissinger et al. 2016 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1874778716300137
Citation: Theissinger, K., Falckenhayn, C., Blande, D., Toljamo, A., Gutekunst, J., Makkonen, J., … & Kokko, H. (2016). De Novo assembly and annotation of the freshwater crayfish Astacus astacus transcriptome. Marine Genomics, 28, 7-10.
My first run of BUSCO for original assembly, I was getting this repeated errors in my slurm output error file:
“Message: BatchFatalError(AttributeError(“‘NoneType’ object has no attribute ‘hmmer_results_lines’”))”
The issue was that the above script was referencing busco-config.ini which had old versions (based on the old modules) instead of using the installed copy $EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini which has the correct paths. So I changed the line in the script below to use the new correct path and it began to run!
There was also another error that the metazoa_odb10 file was an old version and to make sure BUSCO always updates these file versions, we need to use the command -l metazoa_odb10 instead of a set file path for BUSCO to automatically update the versions. Further explanation could be found in the download and automatically update lineaages BUSCO guide section.
Run updated for original assembly:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="busco"
#SBATCH --time="100:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes 1 --ntasks-per-node=20
#SBATCH --mem=250G
##SBATCH --output="busco-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
##SBATCH --export=NONE
echo "START" $(date)
labbase=/data/putnamlab
busco_shared="${labbase}/shared/busco"
[ -z "$query" ] && query="${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trinity_out_dir/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta" # set this to the query (genome/transcriptome) you are running
[ -z "$db_to_compare" ] && db_to_compare="${busco_shared}/downloads/lineages/metazoa_odb10"
source "${busco_shared}/scripts/busco_init.sh" # sets up the modules required for this in the right order
# This will generate output under your $HOME/busco_output
cd "${labbase}/${dbecks}"
busco --config "$EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini" -f -c 20 --long -i "${query}" -l metazoa_odb10 -o busco_output -m transcriptome
echo "STOP" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco.sh
Submitted batch job 288779
BUSCO Results for original assembly
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/busco/busco_output
less short_summary.specific.metazoa_odb10.busco_output.txt
# BUSCO version is: 5.2.2
# The lineage dataset is: metazoa_odb10 (Creation date: 2021-02-17, number of genomes: 65, number of BUSCOs: 954)
# Summarized benchmarking in BUSCO notation for file /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trinity_out_dir/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta
# BUSCO was run in mode: transcriptome
***** Results: *****
C:99.9%[S:21.0%,D:78.9%],F:0.1%,M:0.0%,n:954
953 Complete BUSCOs (C)
200 Complete and single-copy BUSCOs (S)
753 Complete and duplicated BUSCOs (D)
1 Fragmented BUSCOs (F)
0 Missing BUSCOs (M)
954 Total BUSCO groups searched
BUSCO completeness looks great. Completeness looks for the presence or absence of highly conserved genes in an assembly. The aim is to have the highest percentage of genes identified in your assembly, with a BUSCO complete score above 95% considered good (we have 99.9% so yay!).
However, the complete and duplicated BUSCOs are high. Transcriptomes and protein sets that are not filtered for isoforms will lead to a high proportion of duplicates. So, next step suggestions:
- Filter for isoforms
- Map to closest genome (Acropora millepora)
- Filter symbiont genes to check if it helps duplication
Want to also run BUSCO for nonstranded and stranded assemblies separate:
Calculate non-stranded BUSCO scores:
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_nonstranded.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="busco_nonstranded"
#SBATCH --time="100:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes 1 --ntasks-per-node=20
#SBATCH --mem=250G
##SBATCH --output="busco-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
##SBATCH --export=NONE
echo "START" $(date)
labbase=/data/putnamlab
busco_shared="${labbase}/shared/busco"
[ -z "$query" ] && query="${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta" # set this to the query (genome/transcriptome) you are running
[ -z "$db_to_compare" ] && db_to_compare="${busco_shared}/downloads/lineages/metazoa_odb10"
source "${busco_shared}/scripts/busco_init.sh" # sets up the modules required for this in the right order
# This will generate output under your $HOME/busco_output
cd "${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/"
busco --config "$EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini" -f -c 20 --long -i "${query}" -l metazoa_odb10 -o busco_output -m transcriptome
echo "STOP" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_nonstranded.sh
Submitted batch job 312932
BUSCO Results for nonstranded assembly
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/busco_nonstranded/busco_output
less short_summary.specific.metazoa_odb10.busco_output.txt
# BUSCO version is: 5.2.2
# The lineage dataset is: metazoa_odb10 (Creation date: 2021-02-17, number of genomes: 65, number of BUSCOs: 954)
# Summarized benchmarking in BUSCO notation for file /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/trinity_out_dir/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta
# BUSCO was run in mode: transcriptome
***** Results: *****
C:97.3%[S:18.9%,D:78.4%],F:1.8%,M:0.9%,n:954
928 Complete BUSCOs (C)
180 Complete and single-copy BUSCOs (S)
748 Complete and duplicated BUSCOs (D)
17 Fragmented BUSCOs (F)
9 Missing BUSCOs (M)
954 Total BUSCO groups searched
Calculate stranded BUSCO scores:
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_stranded.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="busco_stranded"
#SBATCH --time="100:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes 1 --ntasks-per-node=20
#SBATCH --mem=250G
##SBATCH --output="busco-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
##SBATCH --export=NONE
echo "START" $(date)
labbase=/data/putnamlab
busco_shared="${labbase}/shared/busco"
[ -z "$query" ] && query="${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta" # set this to the query (genome/transcriptome) you are running
[ -z "$db_to_compare" ] && db_to_compare="${busco_shared}/downloads/lineages/metazoa_odb10"
source "${busco_shared}/scripts/busco_init.sh" # sets up the modules required for this in the right order
# This will generate output under your $HOME/busco_output
cd "${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/"
busco --config "$EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini" -f -c 20 --long -i "${query}" -l metazoa_odb10 -o busco_output -m transcriptome
echo "STOP" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_stranded.sh
Submitted batch job 313009
BUSCO Results for stranded assembly
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/busco_nonstranded/busco_output
less short_summary.specific.metazoa_odb10.busco_output.txt
# BUSCO version is: 5.2.2
# The lineage dataset is: metazoa_odb10 (Creation date: 2024-01-08, number of genomes: 65, number of BUSCOs: 954)
# Summarized benchmarking in BUSCO notation for file /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta
# BUSCO was run in mode: transcriptome
***** Results: *****
C:99.8%[S:23.9%,D:75.9%],F:0.2%,M:0.0%,n:954
952 Complete BUSCOs (C)
228 Complete and single-copy BUSCOs (S)
724 Complete and duplicated BUSCOs (D)
2 Fragmented BUSCOs (F)
0 Missing BUSCOs (M)
954 Total BUSCO groups searched
c) Assess the completeness and unique transcripts between the non-stranded and stranded de novo transcriptomes using NCBI nucleotide BLAST to compare the nucleotide sequences of our transcriptomes
Create a script to run the blastn process on both transcriptomes:
nano blast_transcriptomes.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="trans_blastn"
#SBATCH --time="04:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes 1 --ntasks-per-node=20
#SBATCH --mem=250G
##SBATCH --output="blastn-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/ref_trans_blast
##SBATCH --export=NONE
module load BLAST+/2.15.0-gompi-2023a
# Create BLAST databases
makeblastdb -in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -dbtype nucl -out non_stranded_db
makeblastdb -in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -dbtype nucl -out stranded_db
# Run BLAST searches
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db stranded_db -out nonstranded_blast.out -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-5
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db non_stranded_db -out stranded_blast.out -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-5
Submitted batch job 323906
Create a Python script to parse the BLAST results and identify unique and common transcripts:
Enter interactive mode on ssh$ by typing interactive
Enter: module load SciPy-bundle
Then run script below: python parse_blast_results.py
nano parse_blast_results.py
import pandas as pd
# Load BLAST results
nonstranded = pd.read_csv('nonstranded_blast.out', sep='\t', header=None)
stranded = pd.read_csv('stranded_blast.out', sep='\t', header=None)
# Rename columns for clarity
columns = ['qseqid', 'sseqid', 'pident', 'length', 'mismatch', 'gapopen', 'qstart', 'qend', 'sstart', 'send', 'evalue', 'bitscore']
nonstranded.columns = columns
stranded.columns = columns
# Identify unique transcripts in non-stranded transcriptome
unique_non_stranded = set(nonstranded['qseqid']) - set(stranded['sseqid'])
# Identify unique transcripts in stranded transcriptome
unique_stranded = set(stranded['qseqid']) - set(nonstranded['sseqid'])
# Output results
with open('unique_non_stranded.txt', 'w') as f:
for transcript in unique_non_stranded:
f.write(transcript + '\n')
with open('unique_stranded.txt', 'w') as f:
for transcript in unique_stranded:
f.write(transcript + '\n')
# Print results
print("Unique non-stranded transcripts:
{}".format(len(unique_non_stranded)))
print("Unique stranded transcripts: {}".format(len(unique_stranded)))
# Print results
print "Unique non-stranded transcripts: 341
print "Unique stranded transcripts: 1049
8) Remove contaminants from both stranded and nonstranded assembly
My next step is to remove any contaminant reads from the reference transcriptomes (stranded and nonstranded). Jill already did this so following her instructions from her notebook post. From Young et al. 2024: “Raw HiFi reads first underwent a contamination screening, following the methodology in [68], using BLASTn [32, 68] against the assembled mitochondrial O. faveolata genome and the following databases: common eukaryote contaminant sequences (ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/pub/kitts/contam_in_euks.fa.gz), NCBI viral (ref_ viruses_rep_genomes) and prokaryote (ref_prok_rep_ genomes) representative genome sets”.
Create a folder for output data from removing contaminants:
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/
mkdir contam_remove
Download contaminant data sets:
Eukaryote contaminants:
wget ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/kitts/contam_in_euks.fa.gz
gunzip contam_in_euks.fa.gz
For the viral and prokaryote datasets:
There’s a file /data/shared/ncbi-db/.ncbirc that gets updated to point to the current directory, which the blast* tools will automatically pick up, so you can just do -db ref_prok_rep_ genomes, for example.
For other tools that can read the ncbi databases, you can use blastdb_path -db ref_viruses_rep_genomes to get the path, although for some reason with the nr database you need to specify -dbtype prot, i.e., blastdb_path -db nr -dbtype prot.
Now I ran run a script that blasts the stranded and nonstranded references against these sequences. In /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts, nano blast_contam_euk.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
module load BLAST+/2.13.0-gompi-2022a
echo "BLASTing reference transcriptomes against eukaryote contaminant sequences" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -subject /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/contam_in_euks.fa -task megablast -outfmt 6 -evalue 4 -perc_identity 90 -num_threads 15 -out /stranded/contaminant_hits_euks_rr_stranded.txt
echo "BLAST complete, remove contaminant seqs from stranded" $(date)
awk '{ if( ($4 >= 50 && $4 <= 99 && $3 >=98 ) ||
($4 >= 100 && $4 <= 199 && $3 >= 94 ) ||
($4 >= 200 && $3 >= 90) ) {print $0}
}' contaminant_hits_euks_rr_stranded.txt > contaminants_pass_filter_euks_rr_stranded.txt
echo "Contaminant seqs removed from stranded assembly" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -subject /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/contam_in_euks.fa -task megablast -outfmt 6 -evalue 4 -perc_identity 90 -num_threads 15 -out /nonstranded/contaminant_hits_euks_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "BLAST complete, remove contaminant seqs from nonstranded" $(date)
awk '{ if( ($4 >= 50 && $4 <= 99 && $3 >=98 ) ||
($4 >= 100 && $4 <= 199 && $3 >= 94 ) ||
($4 >= 200 && $3 >= 90) ) {print $0}
}' contaminant_hits_euks_rr_nonstranded.txt > contaminants_pass_filter_euks_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "Contaminant seqs removed from nonstranded assembly" $(date)
Submitted batch job 328533 at 13:36 07/02, ran in about three minutes
I looked at the contamination hits in R. See code here.
Now I can move forward with the blasting against viral and prok genomes. In the scripts folder: nano blastn_viral.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
module load BLAST+/2.13.0-gompi-2022a
echo "Blasting stranded transcriptome reference against viral genomes to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db ref_viruses_rep_genomes -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out stranded/viral_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
echo "Blast complete!" $(date)
echo "Blasting nonstranded transcriptome reference against viral genomes to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db ref_viruses_rep_genomes -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out nonstranded/viral_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "Blast complete!" $(date)
Submitted batch job 328556 at 14:05 07/02, took about thirty minutes
I looked at the contamination hits in R. See code here.
In the scripts folder: nano blastn_prok.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
module load BLAST+/2.13.0-gompi-2022a
echo "Blasting stranded transcriptome reference against prokaryote genomes to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db ref_prok_rep_genomes -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out stranded/prok_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
echo "Blast complete!" $(date)
echo "Blasting nonstranded transcriptome reference against prokaryote genomes to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db ref_prok_rep_genomes -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out nonstranded/prok_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "Blast complete!" $(date)
Submitted batch job 328594 at 14:05 07/02 took about thirty minutes
Cat the prok and viral results together and remove anything that has a bit score <1000.
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded
cat viral_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt prok_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt > all_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
awk '$12 > 1000 {print $0}' all_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt > contaminant_hits_pv_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
wc -l contaminant_hits_pv_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
#154867
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded
cat viral_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt prok_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt > all_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
awk '$12 > 1000 {print $0}' all_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt > contaminant_hits_pv_passfilter_rr_nonstranded.txt
wc -l contaminant_hits_pv_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
#1979
Similarly to what I did above, I looked at the contamination hits in R. See code here.
Submitted batch job 328558 at 14:11 07/02
I also need to blast the symbiont genome information. Based on the ITS2 data, the Acropora spp from the Manava site have mostly A1 and D1 symbionts, so I’ll be using the A1 genome and the D1 genome.
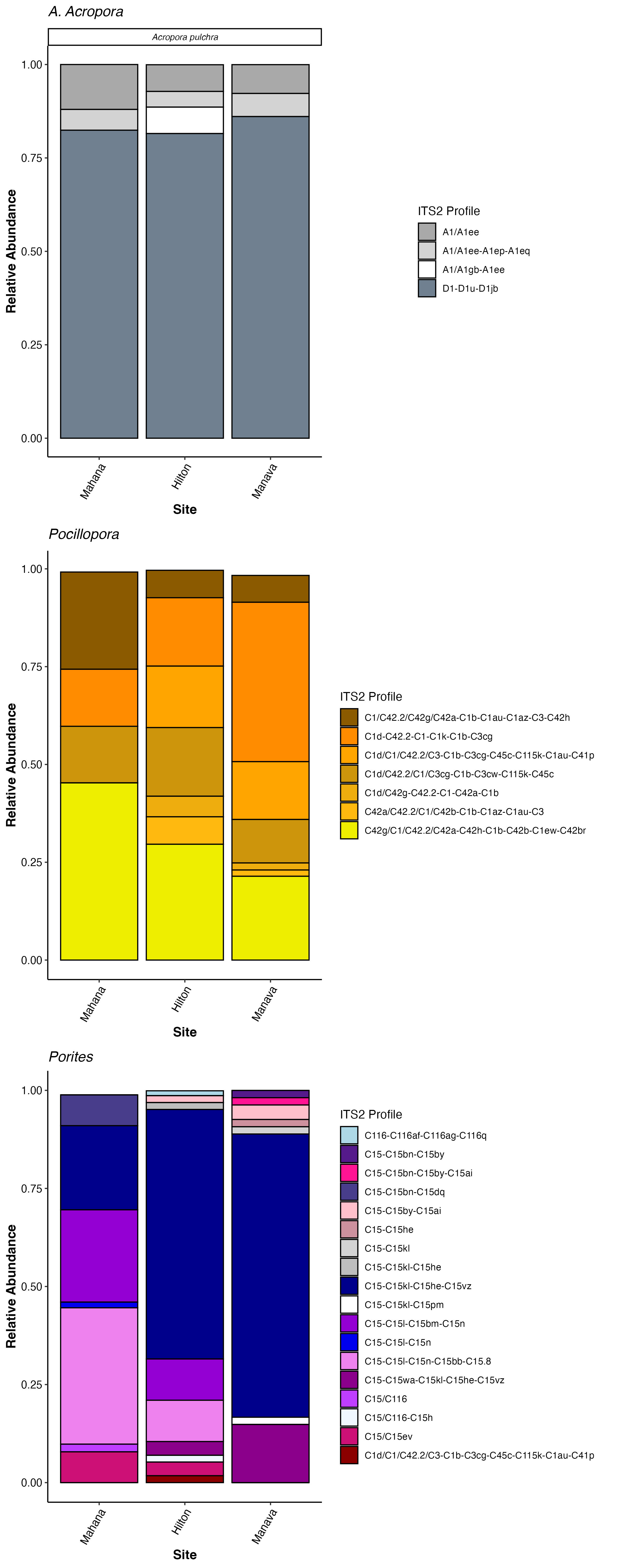
Going to blast to sym genomes now. First download them:
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw
wget http://smic.reefgenomics.org/download/Smic.genome.scaffold.final.fa.gz
wget https://marinegenomics.oist.jp/symbd/download/102_symbd_genome_scaffold.fa.gz
gunzip Smic.genome.scaffold.final.fa.gz
gunzip 102_symbd_genome_scaffold.fa.gz
In the assembly scripts folder: nano blastn_sym.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
module load BLAST+/2.13.0-gompi-2022a
echo "Build A1 seq db" $(date)
makeblastdb -in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/Smic.genome.scaffold.final.fa -dbtype nucl -out /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/A1_db
echo "Build D1 seq db" $(date)
makeblastdb -in /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/102_symbd_genome_scaffold.fa -dbtype nucl -out /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/D1_db
echo "Blasting stranded transcriptome reference reads against symbiont A1 genome to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/A1_db -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out stranded/sym_A1_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
echo "A1 blast complete! Now blasting stranded transcriptome reference reads against symbiont D1 genome to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/D1_db -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out stranded/sym_D1_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
echo "Blasting nonstranded transcriptome reference reads against symbiont A1 genome to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/A1_db -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out nonstranded/sym_A1_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "A1 blast complete! Now blasting nonstranded transcriptome reference reads against symbiont D1 genome to look for contaminants" $(date)
blastn -query /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta -db /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/raw/D1_db -outfmt 6 -evalue 1e-4 -perc_identity 90 -out nonstranded/sym_D1_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
echo "D1 blast complete!"$(date)
Submitted batch job 328568
Cat the sym blast results together for stranded and nonstranded and remove anything that has a bit score <1000.
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded
cat sym_A1_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt sym_D1_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt > sym_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt
awk '$12 > 1000 {print $0}' sym_contaminant_hits_rr_stranded.txt > contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
wc -l contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
# 10742 contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_stranded.txt
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded
cat sym_A1_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt sym_D1_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt > sym_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt
awk '$12 > 1000 {print $0}' sym_contaminant_hits_rr_nonstranded.txt > contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_nonstranded.txt
wc -l contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_nonstranded.txt
# 11681 contaminant_hits_sym_passfilter_rr_nonstranded.txt
Make transcript length .txt files for stranded and nonstranded references:
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} /^>/ {if (seq_length > 0) print transcript_id, seq_length; split($1, a, " "); transcript_id = substr(a[1], 2); seq_length = 0; next} {seq_length += length($0)} END {if (seq_length > 0) print transcript_id, seq_length}' trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta | sort -k2 -nr > transcript_lengths_stranded.txt
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} /^>/ {if (seq_length > 0) print transcript_id, seq_length; split($1, a, " "); transcript_id = substr(a[1], 2); seq_length = 0; next} {seq_length += length($0)} END {if (seq_length > 0) print transcript_id, seq_length}' trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta | sort -k2 -nr > transcript_lengths_nonstranded.txt
Pretty clean when bit scores <1000 are removed. Copy this data onto my computer and remove the contaminants in the R script.
Copy the files all_contam_rem_good_strand_read_list.txt and all_contam_rem_good_nonstrand_read_list.txt that were generated from the R code mentioned above. These specific files were written starting on line 257 and 509. It contains the reads that have passed contamination filtering. I copied each file into cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded and cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded
wc -l all_contam_rem_good_strand_read_list.txt
962995 all_contam_rem_good_strand_read_list.txt
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded
wc -l all_contam_rem_good_nonstrand_read_list.txt
566,929 all_contam_rem_good_nonstrand_read_list.txt
The vast majority of the transcripts are retained after contamination filtering, which is a good sign of high quality sequencing. My next step is to subset the raw stranded and nonstranded transcriptome fasta files to remove the contaminants identified above. I can do this with the seqtk subseq command. In the scripts folder: nano subseq.sh
But first, I need to remove the length information from the all_contam_rem_good_strand_read_list.txt and all_contam_rem_good_nonstrand_read_list.txt files
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded
awk '{$2=""; print $0}' all_contam_rem_good_strand_read_list.txt > output_file_strand.txt
wc -l 962,995 output_file_strand.txt
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded
awk '{$2=""; print $0}' all_contam_rem_good_nonstrand_read_list.txt > output_file_nonstrand.txt
wc -l 566929 output_file_nonstrand.txt
Write script to subset the raw stranded and nonstranded fasta files to remove the contaminants identified above.
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts
nano subseq.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL #email you when job starts, stops and/or fails
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu #your email to send notifications
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
module load seqtk/1.3-GCC-9.3.0
echo "Subsetting stranded transcripts that passed contamination filtering" $(date)
awk 'NR==FNR{ids[$1]; next} /^>/{f=0; for(i in ids) if(index($1, i)) {f=1; break}} f' \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/stranded/output_file_strand.txt \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta \
| seqtk seq -l0 > /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/strand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta
echo "Subsetting complete stranded!" $(date)
echo "Subsetting nonstranded transcripts that passed contamination filtering" $(date)
awk 'NR==FNR{ids[$1]; next} /^>/{f=0; for(i in ids) if(index($1, i)) {f=1; break}} f' \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/contam_remove/nonstranded/output_file_nonstrand.txt \
/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/trinity_out_dir.Trinity.fasta \
| seqtk seq -l0 > /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/nonstrand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta
echo "Subsetting complete nonstranded!" $(date)
Submitted batch job 329322 at 9:48
Identify the unique transcript IDs found in the nonstranded assemmbly not found in the stranded assembly
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/
mkdir final_assembly
cd final_assembly
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/concat.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 100:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=10
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL # email notifications
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu # your email
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly
#SBATCH -o slurm-%j.out
#SBATCH -e slurm-%j.error
# Load necessary modules
module load SeqKit/2.3.1
# Define file paths
UNIQUE_IDS="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/ref_trans_blast/unique_non_stranded.txt"
NONSTRANDED_FASTA="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/nonstranded_output/nonstrand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta"
STRANDED_FASTA="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/strand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta"
OUTPUT_FASTA="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/combined_assemblies.fasta"
# Extract unique non-stranded sequences
seqkit grep -f $UNIQUE_IDS $NONSTRANDED_FASTA > unique_non_stranded_sequences.fasta
# Concatenate the unique non-stranded sequences with the stranded sequences
cat unique_non_stranded_sequences.fasta $STRANDED_FASTA > $OUTPUT_FASTA
# Clean up intermediate files
rm unique_non_stranded_sequences.fasta
echo "Unique non-stranded sequences have been extracted and concatenated with the stranded sequences."
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/concat.sh
Submitted batch job 332872
# look for any duplicate IDs in newly assembled .fasta:
grep "^>" /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/combined_assemblies.fasta | sort | uniq -d
# two duplicates found:
>TRINITY_DN189409_c0_g1_i1 len=211 path=[0:0-210]
>TRINITY_DN297413_c0_g1_i1 len=237 path=[0:0-236]
# removed two duplicates:
awk '/^>/ {if(seen[$0]++) next} {print}' combined_assemblies.fasta > combined_assemblies_cleaned.fasta
# remove duplicates with different lengths, the one with length 277 came from nonstranded assembly:
awk '/^>/ {if ($0 == ">TRINITY_DN113515_c0_g1_i1 len=277 path=[0:0-276]") {p=0} else {p=1}} p' combined_assemblies.fasta > cleaned_assemblies.fasta
# check number of transcripts in final assembly:
grep -c "^>" /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/combined_assemblies.fasta
963413 which makes sense because stranded output fasta had 963075 and 341 unique nonstranded minus the three duplicates
Deciding to move forward with just the stranded assembly, as not many more being added with the nonstranded, which can cause downstream errors later in alignment when stranded needs to be specified.
Run BUSCO for final stranded assembly
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_final.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="busco_final"
#SBATCH --time="100:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=20
#SBATCH --mem=120G
##SBATCH --output="busco-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
##SBATCH --export=NONE
echo "START" $(date)
labbase=/data/putnamlab
busco_shared="${labbase}/shared/busco"
[ -z "$query" ] && query="${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/stranded_output/strand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta" # set this to the query (genome/transcriptome) you are running
source "${busco_shared}/scripts/busco_init.sh" # sets up the modules required for this in the right order
# This will generate output under your $HOME/busco_output
cd "${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/"
# Run BUSCO with the --offline flag and specify the download path
busco --config "$EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini" -f -c 20 -i "${query}" -l metazoa_odb10 -o busco_output -m transcriptome --offline --download_path "${busco_shared}/downloads/"
echo "STOP" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_final.sh
Submitted batch job 334841
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/busco_output
less short_summary.specific.metazoa_odb10.busco_output.txt
***** Results: *****
C:99.8%[S:23.8%,D:76.0%],F:0.1%,M:0.1%,n:954
952 Complete BUSCOs (C)
227 Complete and single-copy BUSCOs (S)
725 Complete and duplicated BUSCOs (D)
1 Fragmented BUSCOs (F)
1 Missing BUSCOs (M)
954 Total BUSCO groups searched
9) Use CD-HIT to reduce redundancy and improve transcriptome assembly quality
a) Run CD-HIT-EST
CD-HIT-EST stands for Cluster Database at High Identity with Tolerance for ESTs (Expressed Sequence Tags). The program (cd-hit-est) takes a FASTA format sequence database as input and produces a set of ‘non-redundant’ (nr) representative sequences as output. The goal is to reduce the overall size of the database while preserving sequence information by clustering sequences that are highly similar. This process eliminates redundancy by grouping similar sequences into clusters, with only one representative sequence retained per cluster. The resulting database is called non-redundant (nr) as it contains unique representatives of similar sequences, thus simplifying the dataset and focusing on diversity within the data. Essentially, cd-hit-est organizes sequences into clusters, reducing redundancy and making it easier to analyze large sequence datasets.
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/cd-hit-est.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 6-00:00:00 # Time limit in days-hours:minutes:seconds
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=8 # Adjusted to match -T
#SBATCH --output=slurm-%A.out
# Load CD-HIT module
module load CD-HIT/4.8.1-GCC-11.3.0
# Define input and output file paths
INPUT_FILE="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/strand_rr_allcontam_rem.fasta"
OUTPUT_FILE="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT/stranded_assembly_cdhit.fasta"
# Run CD-HIT
cd-hit-est -i $INPUT_FILE -o $OUTPUT_FILE -c 0.95 -n 10 -d 0 -M 16000 -T 8
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/cd-hit-est.sh
Submitted batch job 334849
CD-HIT-EST Output file is: stranded_assembly_cdhit.fasta
total seq: 963075
longest and shortest : 51090 and 164
Total letters: 625126251
Sequences have been sorted
Approximated minimal memory consumption:
Sequence : 759M
Buffer : 8 X 34M = 275M
Table : 2 X 32M = 64M
Miscellaneous : 17M
Total : 1116M
b) Asses CD-HIT-EST output with N50 and BUSCO
Run N50 on cdhit assembly:
/opt/software/Trinity/2.15.1-foss-2022a/trinityrnaseq-v2.15.1/util/TrinityStats.pl stranded_assembly_cdhit.fasta > trinity_cdhit_assembly_stats
################################
## Counts of transcripts, etc.
################################
Total trinity 'genes': 626101
Total trinity transcripts: 780970
Percent GC: 44.37
########################################
Stats based on ALL transcript contigs:
########################################
Contig N10: 3595
Contig N20: 2345
Contig N30: 1642
Contig N40: 1154
Contig N50: 812
Median contig length: 343
Average contig: 590.67
Total assembled bases: 461293650
The N10 through N50 values are shown computed based on all assembled contigs. In this example, 10% of the assembled bases are found in transcript contigs at least 3,594 bases in length (N10 value), and the N50 value indicates that at least half the assembled bases are found in contigs that are at least 812 bases in length.
The contig N50 values can often be exaggerated due to an assembly program generating too many transcript isoforms, especially for the longer transcripts. To mitigate this effect, the script will also compute the Nx values based on using only the single longest isoform per ‘gene’:
#####################################################
## Stats based on ONLY LONGEST ISOFORM per 'GENE':
#####################################################
Contig N10: 3374
Contig N20: 2085
Contig N30: 1393
Contig N40: 950
Contig N50: 673
Median contig length: 321
Average contig: 535.54
Total assembled bases: 335300440
You can see that the Nx values based on the single longest isoform per gene are lower than the Nx stats based on all assembled contigs, as expected, and even though the Nx statistic is really not a reliable indicator of the quality of a transcriptome assembly, the Nx value based on using the longest isoform per gene is perhaps better for reasons described above.
Run BUSCO on cdhit assembly:
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_cdhit.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name="busco_final"
#SBATCH --time="100:00:00"
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=36
#SBATCH --mem=120G
##SBATCH --output="busco-%u-%x-%j"
##SBATCH --account=putnamlab
##SBATCH --export=NONE
echo "START" $(date)
export NUMEXPR_MAX_THREADS=36
labbase=/data/putnamlab
busco_shared="${labbase}/shared/busco"
[ -z "$query" ] && query="${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT/stranded_assembly_cdhit.fasta" # set this to the query (genome/transcriptome) you are running
source "${busco_shared}/scripts/busco_init.sh" # sets up the modules required for this in the right order
# This will generate output under your $HOME/busco_output
cd "${labbase}/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT/"
# Run BUSCO with the --offline flag and specify the download path
busco --config "$EBROOTBUSCO/config/config.ini" -f -c 20 -i "${query}" -l metazoa_odb10 -o busco_output -m transcriptome --offline --download_path "${busco_shared}/downloads/"
echo "STOP" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/busco_cdhit.sh
Submitted batch job 334850
cd /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT/busco_output
less short_summary.specific.metazoa_odb10.busco_output.txt
--------------------------------------------------
|Results from dataset metazoa_odb10 |
--------------------------------------------------
|C:99.8%[S:29.4%,D:70.4%],F:0.1%,M:0.1%,n:954 |
|952 Complete BUSCOs (C) |
|280 Complete and single-copy BUSCOs (S) |
|672 Complete and duplicated BUSCOs (D) |
|1 Fragmented BUSCOs (F) |
|1 Missing BUSCOs (M) |
|954 Total BUSCO groups searched |
--------------------------------------------------
10) Map to Acropora pulchra incomplete reference genome
a) Obtain Reference Genome and Create Folder Structure
I am using the Moorea, French Polynesia incomplete Acropora pulchra genome to compare alignment statistics.
Location on Andromeda, the HPC server for URI:
cd /data/putnamlab/jillashey/Apul_Genome/assembly/data/apul.hifiasm.s55_pa.p_ctg.fa.k32.w100.z1000.ntLink.5rounds.fa
Bioinformatic workflow made by Jill Ashey as she works on reference genome assembly
b) Generate genome build
HiSat2 Align reads to refernece transcriptome
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/Hisat2_genome_build_Apul.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 24:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=100GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul
#SBATCH --error="script_error"
#SBATCH --output="output_script"
module load HISAT2/2.2.1-gompi-2022a
# index the reference genome for Apul output index to working directory
hisat2-build -f /data/putnamlab/jillashey/Apul_Genome/assembly/data/apul.hifiasm.s55_pa.p_ctg.fa.k32.w100.z1000.ntLink.5rounds.fa ./Apul_ref # called the reference genome (scaffolds)
echo "Reference genome indexed. Starting alignment" $(date)
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/Hisat2_genome_build_Apul.sh
Submitted batch job 333445
c) Align transcriptome to genome
mkdir data/mapped
- Trinity assembly in FASTA format and you want to align it to a reference genome, you would generally use a different tool like BLAT, GMAP, or minimap2, as they are designed for aligning longer sequences like transcripts or assembled contigs.
- Using minimap2
- In this example, -ax splice specifies that the input is spliced transcripts, -uf specifies the reference genome, and the output is redirected to a SAM file (Trinity_aligned.sam).
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/minimap_align2_Apul.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 72:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=5
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=500GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul/mapped
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=3
#SBATCH --error="script_error"
#SBATCH --output="output_script"
module load minimap2/2.24-GCCcore-11.3.0
#Aligning to Trinity output file
minimap2 -d /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul/reference_index.idx /data/putnamlab/jillashey/Apul_Genome/assembly/data/apul.hifiasm.s55_pa.p_ctg.fa.k32.w100.z1000.ntLink.5rounds.fa
minimap2 -ax splice -uf /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul/reference_index.idx /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/output/final_assembly/CD-HIT/stranded_assembly_cdhit.fasta > trinity_aligned.sam
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/minimap_align2_Apul.sh
Submitted batch job 333831
d) Sort and convert sam to bam and check number of mapped reads and mapping percentages
- Explanation:
- samtools sort -o Trinity_aligned.sorted.bam Trinity_aligned.sam: This command sorts the SAM file and creates a sorted BAM file (Trinity_aligned.sorted.bam).
- samtools index Trinity_aligned.sorted.bam: This command creates an index for the sorted BAM file. The index file (Trinity_aligned.sorted.bam.bai) is necessary for certain operations and viewers.
- samtools flagstat Trinity_aligned.sorted.bam: This command generates statistics about the alignment, including the number of mapped reads and mapping percentages.
nano /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/SAMtoBAM_Apul.sh
#There will be lots of .tmp file versions in your folder, this is normal while this script runs and they should delete at the end to make one sorted.bam file
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -t 72:00:00
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=8
#SBATCH --export=NONE
#SBATCH --mem=120GB
#SBATCH --mail-type=BEGIN,END,FAIL
#SBATCH --mail-user=danielle_becker@uri.edu
#SBATCH --account=putnamlab
#SBATCH -D /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul/mapped
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=3
#SBATCH --error="script_error"
#SBATCH --output="output_script"
module load SAMtools/1.16.1-GCC-11.3.0 #Preparation of alignment for assembly: SAMtools
# Directory containing SAM files
sam_directory="/data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/data/ref_genome_Apul/mapped"
# Process each SAM file in the directory
for sam_file in "$sam_directory"/*.sam; do
if [ -f "$sam_file" ]; then
# Extract sample name from the file
sample_name=$(basename "${sam_file%.sam}")
# Step 1: Sort the SAM file and convert to BAM
samtools sort -o "${sam_directory}/${sample_name}_sorted.bam" "$sam_file"
# Step 2: Index the BAM file
samtools index "${sam_directory}/${sample_name}_sorted.bam"
# Step 3: Check Mapping Statistics
samtools flagstat "${sam_directory}/${sample_name}_sorted.bam" > "${sam_directory}/${sample_name}_flagstat.txt"
echo "Processed: ${sample_name}"
echo "------------------------"
fi
done
sbatch /data/putnamlab/dbecks/DeNovo_transcriptome/2023_A.pul/scripts/SAMtoBAM_Apul.sh
Submitted batch job 334118
Mapping Percentages
interactive
module load SAMtools/1.9-foss-2018b #Preparation of alignment for assembly: SAMtools
for i in *sorted.bam; do
echo "${i}" >> mapped_reads_counts_trinity
samtools flagstat ${i} | grep "mapped (" >> mapped_reads_counts_trinity
done
trinity_aligned_sorted.bam
756286 + 0 mapped (67.93% : N/A)
Transcriptome reference assembly complete! Next step is to make the functional annotation, all steps outlined in the Acropora pulchra functional annotation workflow and complete transcript expression quantification using RSEM for gene counts in this workflow.
